If you use an Apple iPhone, iPad or other iDevice, now would be an excellent time to ensure that the machine is running the latest version of Apple’s mobile operating system — version 9.3.1. Failing to do so could expose your devices to automated threats capable of rendering them unresponsive and perhaps forever useless.
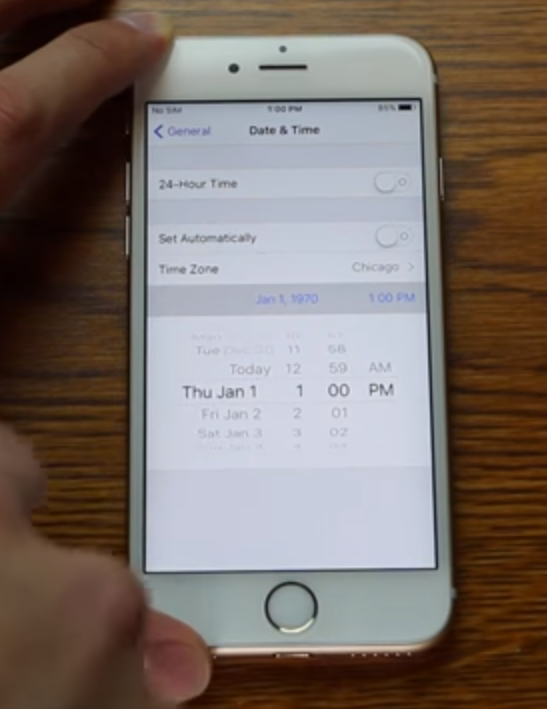
Zach Straley demonstrating the fatal Jan. 1, 1970 bug. Don’t try this at home!
On Feb. 11, 2016, researcher Zach Straley posted a Youtube video exposing his startling and bizarrely simple discovery: Manually setting the date of your iPhone or iPad all the back to January. 1, 1970 will permanently brick the device (don’t try this at home, or against frenemies!).
Now that Apple has patched the flaw that Straley exploited with his fingers, researchers say they’ve proven how easy it would be to automate the attack over a network, so that potential victims would need only to wander within range of a hostile wireless network to have their pricey Apple devices turned into useless bricks.
Not long after Straley’s video began pulling in millions of views, security researchers Patrick Kelley and Matt Harrigan wondered: Could they automate the exploitation of this oddly severe and destructive date bug? The researchers discovered that indeed they could, armed with only $120 of electronics (not counting the cost of the bricked iDevices), a basic understanding of networking, and a familiarity with the way Apple devices connect to wireless networks.
Apple products like the iPad (and virtually all mass-market wireless devices) are designed to automatically connect to wireless networks they have seen before. They do this with a relatively weak level of authentication: If you connect to a network named “Hotspot” once, going forward your device may automatically connect to any open network that also happens to be called “Hotspot.”
For example, to use Starbuck’s free Wi-Fi service, you’ll have to connect to a network called “attwifi”. But once you’ve done that, you won’t ever have to manually connect to a network called “attwifi” ever again. The next time you visit a Starbucks, just pull out your iPad and the device automagically connects.
From an attacker’s perspective, this is a golden opportunity. Why? He only needs to advertise a fake open network called “attwifi” at a spot where large numbers of computer users are known to congregate. Using specialized hardware to amplify his Wi-Fi signal, he can force many users to connect to his (evil) “attwifi” hotspot. From there, he can attempt to inspect, modify or redirect any network traffic for any iPads or other devices that unwittingly connect to his evil network.
For more detailed information please visit Krebs on Security – we listen to him so should you! Krebs is the source of the material above.