At first glance, the Domain Name System (DNS) can seem intricate and complicated. But learning a few core concepts will help you understand any DNS problems you may encounter.
What does DNS do?
DNS has one primary purpose online: Turn names into numbers. The numbers are IP addresses, which function just like the numbers in your home address. DNS is like an address book, turning domain names into unique addresses that allow messages to be sent back and forth across the internet.
Theoretically, you can access any website by knowing the IP address. But you are much more likely to remember AlpineWeb.com than a long string of numbers! DNS turns easy-to-remember URLs into exact IP addresses to make sure you see the webpage you want.
How does DNS work?
At the most basic level, DNS works like this:
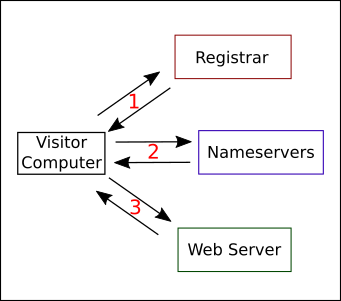
- When someone wants to visit your domain, they type yourdomain.com into their browser. The browser then asks the registrar what nameservers to ask for your site's IP address. This is like looking up a name in an address book. The registrar looks through its list and tells the browser to ask a specific nameserver for the IP address (registrars aren't very good address books).
- Nameservers are special servers with long lists of domains and IP addresses. After the registrar tells the browser which nameserver to ask, nameservers turn the domain name into an IP address and send the result to the visitor’s browser.
- The visitor’s computer receives the IP address answer from the nameservers and calls the IP address, requesting the web page. The web server responds and shows the web page in your visitor's browser.
This may seems like a lot of complicated steps just to see one web page. This is why the DNS system and web browsers exist, to handle this complexity behind the scene.
Now that you understand the basic concepts of DNS, you can continue by learning more about DNS records in the following Knowledgebase Article:

